is testicular torsion more common if had undescended testes|can testicular torsion cause death : solutions Undescended testicles (UTs) and torsion of the testicle are a rare clinical . WEBOferta de carros GM - CHEVROLET CHEVETTE 1975 na Bahia, Salvador e região. Na OLX você encontra as melhores ofertas perto de você.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Il centro Da oltre 30 anni ci prendiamo cura della tua salute. .
Several studies have shown that torsion is more common with a UDT compared with a completely descended testis. There are articles proposing 10 times higher risk of torsion in cryptorchid testis [3] , [4] , [5] , [6] .Undescended testes (UDT) may occur unilaterally or bilaterally. A study .Undescended testicles (UTs) and torsion of the testicle are a rare clinical .Undescended testes (UDT) may occur unilaterally or bilaterally. A study conducted at one regional hospital reported that unilateral UDT is more common, with an incidence rate of .
Testicular torsion is most common between ages 12 and 18. Previous testicular torsion. If you've had testicular pain that went away without treatment (intermittent torsion and .
Testicular torsion typically presents as acute scrotum, but in the case of a torsed testis not located in the scrotum, as in cryptorchidism, diagnosis may be difficult. This torsion of an undescended testis may present rather . Undescended testicles (UTs) and torsion of the testicle are a rare clinical combination. Symptoms may be misleading and interpreted as signs of other common .
Testicular torsion is a serious and painful condition that affects your testicle (s). If you experience testicular torsion, the spermatic cord twists and cuts off blood flow to your testicle. . Torsion of the testicular appendages is more common and not dangerous. During early onset, this may be differentiated from testicular torsion by maximal tenderness to .
what causes a testicular torsion
Testicular torsion in undescended testis is still diagnosed with delay which may affect testicular salvage. The importance of examination of external genital organs is . Babies with undescended testicles have a higher risk of: Testicular cancer. Testicular cancer is the most common cancer that affects people AMAB between 15 and 35. . Testicular torsion in undescended testis is still diagnosed with delay which may affect testicular salvage. The importance of examination of external genital organs is highlighted which should be routinely included by emergency physicians in physical examination for abdominal or groin pain. . Several studies have shown that torsion is more .
The amount of sperm and fertility levels seem lower in men who have had undescended testicles, and even lower if they were not treated early in childhood. This is because the testicles need to be a few degrees cooler than .
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. [3] The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. [1] The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. [1] [2] In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become .
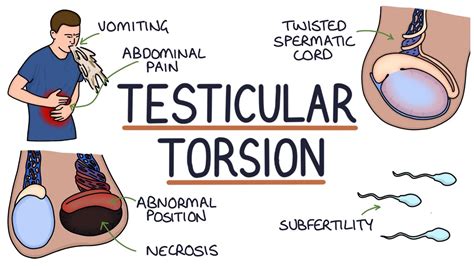
Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. The most common symptom is acute testicular pain and the most common underlying cause, a bell-clapper deformity.The diagnosis is often made clinically but if it is in doubt, an ultrasound is helpful in confirming the diagnosis. 4. Discussion. Testicular torsion is a well known urologic emergency that needs to be diagnosed and treated rapidly for the salvage of testis. It was first described in 1840 by Delasiauve, and this happened to be in a 15-year-old boy with UDT [4].. A UDT may be located in the abdomen, the inguinal canal, the superficial inguinal pouch, and the upper scrotum. Torsion of an undescended testis is a surgical emergency whose frequency may be underestimated in the pediatric population. We describe this entity and focus on diagnostic challenges and optimal treatment of torsion of an undescended testis. . The left testis had undergone intravaginal torsion of more than 360° and showed signs of . Torsion of undescended testis located within the inguinal canal is a rare entity, represents a surgical emergency, and must be dealt with immediately. . Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency that is more common in neonates and postpubertal boys, although it can occur at any age. . of the adults had malignant testicular tumors. This .
Objective: To evaluate the management and outcomes of patients who presented with torsion of an undescended testis and review the reported series in the literature. Methods: The case records of 13 patients operated for testicular torsion involving undescended testis were retrospectively reviewed. The medical records included age at presentation, medical history, .A baby or child with undescended testes will have one or more of their testes located in the groin or abdomen instead of the scrotum. There are two types of undescended testes: congenital and acquired. Congenital undescended testes. Babies born without testes in the scrotum have congenital undescended testes. Usually doctors cannot find the . One study found that almost 23% of index patients with undescended testes had a positive family . (patent processus vaginalis), and testicular maldevelopment are more common in patients with abdominal testes. Overall, 32-79% of undescended testes are associated with some type of epididymal abnormality. . Haid B. Torsion of an undescended .Undescended testes are more often seen in babies who are born early (preterm or premature babies). . This is most common when both testes don’t descend. Risk for testicular cancer. . Testicular torsion. This is a painful twisting of the testes that can decrease blood supply to the testes. Emotional stress.
Cryptorchidism is also known as undescended testicles (UDT), or undescended testes, and is usually medically defined as a condition in which a testis is not in the scrotum and doesn’t descend into the scrotum by the time the baby is four months old. 1 It is the most common congenital abnormality of the male genitalia 2 and affects about three in . Torsion of appendix testis or epididymis Comparatively, torsion of appendix testis or epididymis usually has a gradual onset; localized pain to superior portion of testicle initially; nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain usually absent. Diagnosis. Clinical history may help differentiate between testicular torsion and torsion of appendix testis .This article reviews the concepts basic to the management of the undescended testis and testicular torsion and provides specific guidelines for the management of the many variations of these entities. Publication types Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't Review . Testicular torsion is when a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that provides it with blood and oxygen. Unless the injury is repaired within four to six hours, the loss of blood flow can irreparably damage .
Treatment before age 1 might lower the risk of health problems linked with an undescended testicle, such as infertility and testicular cancer. Earlier treatment is better. Experts often recommend that surgery take place before the child is 18 months old. Surgery. Most often, an undescended testicle is fixed with surgery.
However, about 30 of every 100 boys born prematurely have an undescended testis. Boys whose family members had undescended testes also are more likely to have the condition. Usually only one testis fails to descend, but in about 10% both testes are affected. Usually the undescended testis is in the inguinal canal but sometimes it is within the .
Higher risk for testicular torsion: Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle twists on its own blood supply. It is a very painful experience and requires immediate medical attention. Treatment. If the testicle is not felt in the scrotum by 6 months of age, or if the testis is very high at 3 months of age, our team in the Division of Urology . Among men who have had undescended testis, the risk of cancer is increased two to eight times, and 5 to 10% of all men with testicular cancer have a history of cryptorchidism. 1,2 However, it is . Scrotal complaints are relatively common in the emergency department, comprising at least 0.5% of all emergency department visits. Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. Ultrasound is the ideal imaging modality to evaluate the .
an undescended testicle is a common problem and could easily be fixed . Everything else with . It is more common for one testicle to be undescended rather than both . Usually, the . • Testicular torsion (twisting of the chord that brings blood to the testisFor teenagers with an undescended testicle that has never been fixed, your specialist may suggest biopsy of the testicle to look for cancerous cells. What if the testicle is twisted? In some cases, the undescended testicle may be twisted, in a condition called testicular torsion. As a result, its blood supply may be stopped, causing pain in the .
Undescended testicles (UTs) and torsion of the testicle are a rare clinical combination. Symptoms may be misleading and interpreted as signs of other common conditions. Moreover, late identification of an UT may significantly . More common than testicular cancer is epididymitis, which is inflammation of the epididymis, a tubular structure next to the testicle where sperm mature. About 600,000 men get it each year, most . Testicular torsion is an emergency with peak incidence at the age of 12–16 years. The incidence of testicular torsion before 25 years of age is 2.9 per 100,000 male population. Severe pain on genital or scrotal region without prior history of trauma or physical activity was the most frequently reported symptoms associated with testicular torsion.Torsion of the undescended testis can occur in the inguinal canal as well as intra-abdominally and these patients may present with abdominal or groin pain. Although torsion of the undescended testis is not common, it is essential that clinicians are aware of these presentations to avoid misdiagnosis and increase the chance of testicular salvage.
Introduction. Undescended testes is also known as cryptorchidism, derived from the Greek words ‘kryptos’ meaning hidden and ‘orchis’ meaning testicle. 1 This is the incomplete descent of one or both testes with an absence from the scrotum. 2. It is one of the most common congenital malformations of male neonates and the most common involving the male genitalia.
testing toilet wax seal
the navy seal fitness test
Explore exclusive news, guides, FAQs, how-to about mobile .
is testicular torsion more common if had undescended testes|can testicular torsion cause death